
- May 8, 2024
- Alaa Mostafa
- 0
A Guide to SAP Business One Implementation Methodology
Are you considering implementing SAP Business One? Embarking on this journey requires a well-structured approach to ensure smooth execution and optimal results. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the SAP Business One implementation methodology, offering insights and best practices to help you navigate the process with confidence.
Understanding SAP Business One Implementation Methodology
Implementing SAP Business One is more than just deploying software; it’s a strategic endeavor that impacts your entire organization. The implementation methodology will streamline this process, guiding you through key stages from planning to post-implementation support. Let’s explore the core components:
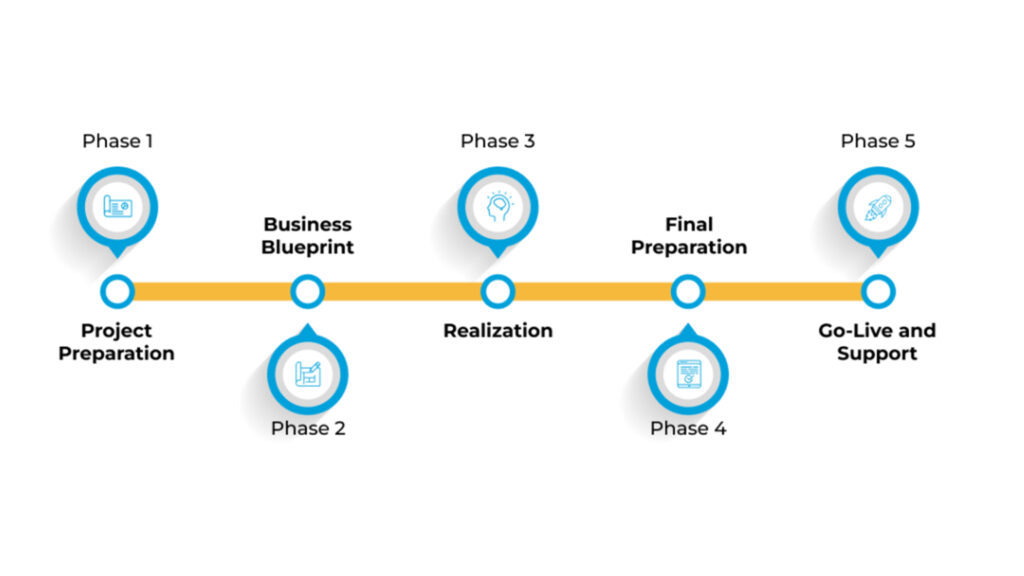
1. Preparation and Planning:
- Define objectives and goals: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with SAP Business One.
- Assess current processes: Evaluate existing workflows and identify areas for improvement.
- Resource allocation: Determine the required resources, including personnel, budget, and timeframes.
2. Business Blueprint:
- Gather requirements: Engage stakeholders to document business processes and specific needs.
- Solution design: Translate requirements into a tailored SAP Business One solution design.
- Prototype creation: Develop prototypes to validate the proposed solution and gather feedback.
3. Realization:
- System configuration: Configure SAP Business One according to the finalized solution design.
- Data migration: Transfer existing data into the new system while ensuring accuracy and integrity.
- Customization and development: Implement any necessary customizations or enhancements to meet unique business requirements.
4. Final Preparation:
- User training: Conduct comprehensive training sessions to empower users with the necessary skills.
- System testing: Perform rigorous testing to validate functionality and identify any potential issues.
- Cut-over planning: Develop a detailed plan for transitioning to the new system, minimizing downtime and disruption.
5. Go-Live and Support:
- Deployment: Execute the cut-over plan and launch SAP Business One into production.
- Post-implementation support: Provide ongoing support to address user queries, resolve issues, and ensure system stability.
- Continuous improvement: Establish processes for monitoring performance and implementing enhancements over time.
Key Considerations for Successful Implementation:
- Executive sponsorship and stakeholder buy-in are critical for driving adoption and securing necessary resources.
- Clear communication and collaboration among project teams, stakeholders, and implementation partners are essential throughout the process.
- Flexibility and adaptability are key as unforeseen challenges may arise during implementation.
- Training and change management efforts are vital to ensure users embrace the new system and maximize its benefits.
Conclusion:
Implementing SAP Business One is a significant undertaking, but the right methodology and approach can yield transformative results for your organization. By following a structured implementation process, aligning with business objectives, and leveraging experienced partners’ expertise, you can confidently navigate the journey to success.
Source: SAP


